A Brief Analysis of Profit Contraction Pressure on Domestic Tinplate Manufacturers
Category: Industry News
Time:2025-09-15
In recent years, the profitability of the domestic tinplate market has experienced fluctuations, showing an overall contraction trend. By analyzing key data from January 2023 to August 2025, the gross profit of manufacturing enterprises declined continuously from a peak of 744.99 yuan/ton in March 2023 to 108.03 yuan/ton in August 2025, a decrease of 85.5%. This trend is not caused by a single factor but is the result of the combined interaction of raw material costs, product prices, and market demand, with weak end-user demand being the main reason for the narrowing profit margins. The author will analyze this in conjunction with specific data:
Preface: In recent years, the profitability of the domestic tinplate market has experienced fluctuations, showing an overall contraction trend. By analyzing key data from January 2023 to August 2025, the gross profit of manufacturing enterprises declined continuously from a peak of 744.99 yuan/ton in March 2023 to 108.03 yuan/ton in August 2025, a drop of 85.5%. This trend is not caused by a single factor but is the result of the combined interaction of raw material costs, product prices, and market demand, with weak end-user demand being the main reason for the narrowing profit margin. The author will analyze this with specific data:
From the cost structure perspective, the production cost of tinplate mainly consists of hot-rolled C material and tin ingots. As shown in the chart, the comprehensive index of the tinplate substrate shows an overall fluctuating downward trend, falling from 4305.90 yuan/ton in January 2023 to 3608.50 yuan/ton in August 2025, a decrease of about 16%. This downward trend theoretically should bring cost advantages to manufacturers, but the simultaneous rise in tin ingot prices offset this advantage. Tin ingot prices rose from 219,583 yuan/ton in January 2023 to 268,274 yuan/ton in August 2025, an increase of over 22%. This caused the cost of tin ingots per ton of steel to increase from 807.27 yuan/ton to 986.27 yuan/ton, adding nearly 180 yuan/ton to production costs. The cost of tinplate was about 6080 yuan/ton at the beginning of 2023 and remained high at 5562 yuan/ton in August 2025, with limited cost reduction. Meanwhile, the average ex-factory price of tinplate continuously dropped from 6650 yuan/ton in January 2023 to 5670 yuan/ton in August 2025, a decrease of about 14.7%. This downward price trend contrasts sharply with the relatively firm cost side, squeezing the gross profit margin.
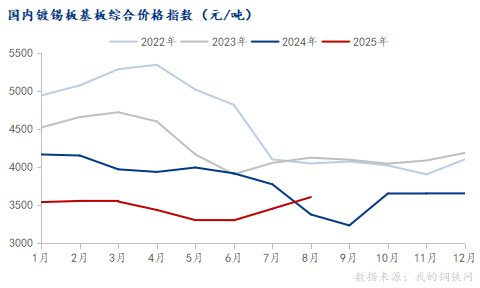
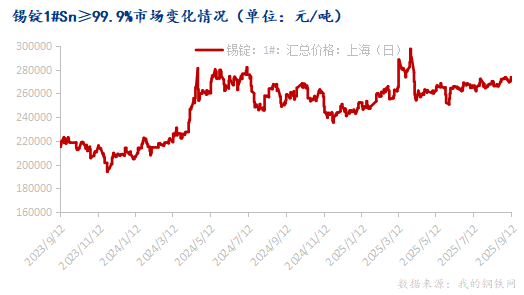
From the timeline perspective, profit levels were relatively high in the first half of 2023, especially peaking in March. During this period, raw material costs were relatively low, while product prices remained at a certain height, providing good profit margins for enterprises. However, starting from the second half of 2023, profit margins began to narrow, and by the second half of 2024, the decline in profits accelerated significantly. Since 2025, gross profits have hovered in a low range of 100-300 yuan/ton, indicating that the industry has entered a stage of minimal profits or even losses for some enterprises.
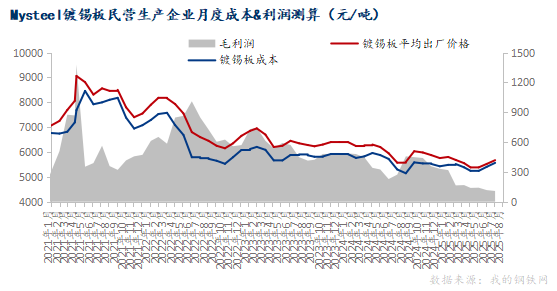
A deeper analysis of the reasons behind the profit decline shows that the primary factor is the mediocre performance of end-market demand. Tinplate is mainly used in industries such as chemicals, canned food, and beverage packaging, and the development speed of these industries directly determines the demand for tinplate. In recent years, with the slowdown in consumption growth and the substitution effect of new packaging materials like aluminum and plastics, the traditional market demand for tinplate has been weak. Insufficient demand has led to intensified market competition, forcing manufacturers to adopt price reduction strategies to maintain market share, making it difficult to pass on raw material cost increases to downstream customers through product price hikes.
Secondly, supply continues to increase, and manufacturers' ex-factory prices remain generally weak. As of the time of writing, according to Mysteel's monitoring of key tinplate manufacturers, the operating rate in August 2025 was 78%, with a capacity utilization rate of 79.86%. Actual tinplate production in August was 466,700 tons, a month-on-month increase of 2,200 tons, and the same factory inventory was 193,100 tons, a month-on-month increase of 1,800 tons. From January to August 2025, domestic tinplate cumulative output was 3.5402 million tons, an increase of about 3.60% compared to the same period last year. The improvement in production line capacity utilization combined with the release of new capacity means that the supply side needs to increase utilization rates to reduce per-ton production costs, while also engaging in fierce market competition by lowering product prices to benefit customers, failing to effectively convert this into enterprise profits.
In summary, the profit decline in the tinplate industry is the result of multiple factors. On the surface, it appears to be a mismatch between raw material costs and product prices, but at a deeper level, it reflects a weak industry supply-demand structure. The rise in tin ingot prices directly pushed up production costs, the decline in hot-rolled C material prices failed to effectively translate into enterprise profits, and the continuous drop in tinplate ex-factory prices reflects weak end-user demand. The future recovery of profitability in the tinplate industry will not only require coordination on the raw material cost side but will also depend on the resilience of downstream demand and the industry's own structural adjustment and upgrading process.
Keywords: A Brief Analysis of Profit Contraction Pressure on Domestic Tinplate Manufacturers
Related Information
Company News
-
Chuangcai’s latest news: Trump puts further pressure on Iran, and coke prices see their first round of increase.
Time:2026-01-29
-
We warmly welcome UAE customers to visit our color-coated and galvanized steel plants.
Time:2026-01-27
-
Warmly celebrate that our Nepalese customer has successfully passed the inspection of all company products.
Time:2026-01-23
-
Chuangcai Group Co., Ltd. launches bright-finish galvanized steel sheets, leading the industry with advanced technology and superior quality.
Time:2026-01-14
-
Warm Celebration of the First Perfect Cooperation between Chuangcai Group Co., Ltd. and Azerbaijani Customers
Time:2025-12-16
-
Warmly celebrate the great success of Chuangcai Group Co., Ltd. at the Dubai exhibition.
Time:2025-12-02
-
Morning reading: The "14th Five-Year" Plan proposal clearly outlines the development direction and opportunities for the steel industry.
Time:2025-10-29
-
Special Meeting on Creative Color Group Corporation's Strategy for Managing Risks in the Indian Market
Time:2025-10-16
-
Warmly celebrate Chuangcai Group Co., Ltd.'s successful participation in Alibaba International's "Heroes Contest, Billion Battle to Fame" high-quality customer negotiation training.
Time:2025-09-15
-
Morning Reading: Iron ore prices rise above $105, first round of coke price reductions implemented
Time:2025-09-09
-
Warmly celebrate Shandong Longjian Board Industry Co., Ltd. for successfully passing the ISO9001 certification
Time:2025-09-05
-
Internal Company International Business Knowledge Collision: Wisdom Integration, Expanding Global Perspectives Together
Time:2025-09-02
-
Two groups of Indian clients visited the factory, securing 3.000 tons of new orders
Time:2025-08-15
-
What industries use galvanized steel sheets? What types are there?
Time:2025-01-08
-
What are the main applications of galvanized materials?
Time:2025-01-08
-
How to distinguish between galvanized sheet and cold-rolled sheet
Time:2025-01-08
-
The difference between galvanized steel sheet and cold-rolled steel sheet
Time:2025-01-08
Industry News
-
Chuangcai’s Interpretation: The Fed’s Future Policy Direction Still Holds Uncertainty—A Brief Analysis of “Interest Rate Cuts, Balance Sheet Reduction, and a Stable U.S. Dollar”
Time:2026-02-03
-
The global precious metals market plunges; China’s Hubei steel mills conduct winter stockpiling surveys.
Time:2026-02-02
-
Chuangcai Latest News: Supply Increase and Demand Decrease for China's Five Major Steel Products, Chief Outlook on February Steel Prices
Time:2026-01-30
-
China Iron and Steel Association: Production Status of Plate and Strip Products from Key Statistical Enterprises as of December 2025
Time:2026-01-28
-
ChuangCai Consulting: Global crude steel production is projected to reach 1849 million tons in 2025, with a general rise in international commodity prices.
Time:2026-01-26
-
What structural changes will occur in China’s steel demand in 2026?
Time:2026-01-23
-
In the fourth quarter of 2025, Fortescue Metals Group in Australia is expected to produce 49.8 million tons of iron ore, a 2% decrease year-on-year.
Time:2026-01-22
-
This year, the enthusiasm for winter stockpiling of construction steel in Shandong Province, China, has cooled down, and winter inventories will continue to decline.
Time:2026-01-21
-
In 2025, China exported 6,690 ships, a year-on-year increase of 16.2%.
Time:2026-01-19
-
International commodity prices are rising across the board, and several countries are urging their citizens to leave Iran.
Time:2026-01-15
-
China’s latest advisory news: Trump says he’s canceling all talks with Iranian officials; steel futures rise in overnight trading.
Time:2026-01-14
-
China Shagang’s scrap steel prices rise by 50 yuan; China Ansteel, Bensteel, and Linggang announce February price adjustments.
Time:2026-01-13
-
The State Council executive meeting deploys policies to boost domestic demand; Zhongtian Steel and Yonggang announce their latest price adjustments.
Time:2026-01-12
-
Pressure Eases, Resilience Remains—A Forecast of the Impact of Global Steel Trade Remedies on China in 2026
Time:2026-01-09
-
Steel has it all wrapped up at the Northeastern University EXP Building in Boston
Time:2026-01-08
-
Steel-Based Zero Energy Building (ZEB) Inaugurated in India
Time:2026-01-07
-
International bulk commodities generally surged, while black commodity futures fell during the night session.
Time:2026-01-06
-
As the price pattern shifts to a narrowing “W” formation and regional coordination strengthens, can the 2026 stainless steel market maintain steady progress?
Time:2026-01-06
-
January cold-rolled prices may trend weaker.
Time:2026-01-06
-
January Steel Market—Pre-Holiday Weak Realities Weigh Down Prices; Black-Steel Sector Awaits “Spring Surge”
Time:2025-12-29
-
Interpreting the Guidance of Import Coal Price Spreads on Domestic Coking Coal Price Volatility (Part 1)
Time:2025-12-29
-
2026 Steel Market Winter Stockpiling Outlook
Time:2025-12-25
-
The countdown for export licenses has begun! Can China’s galvanized sheet exports reach new highs again in 2026?
Time:2025-12-25
-
Li Qiang called for planning a batch of major projects and undertakings that can drive the overall situation.
Time:2025-12-23
-
Value Equilibrium—A 2026 Outlook for China’s Steel Market
Time:2025-12-22
-
The Ministry of Commerce responds to the management of steel export licenses, and Jiangsu’s winter stockpiling of scrap steel shrinks in scale.
Time:2025-12-20
-
2026 Steel Indirect Export Forecast
Time:2025-12-18
-
Analysis of the Impact of Implementing Export License Management for Seamless Pipe Products and Enterprises’ Response Strategies
Time:2025-12-18
-
Luo Tiejun calls for jointly breaking the cycle of involutionary competition; the chief analyst of sheet and strip forecasts January steel prices.
Time:2025-12-16
-
Multiple ministries are promoting measures to combat “involution”; interpretation of the management of steel export licenses.
Time:2025-12-16
-
The Federal Reserve cut interest rates by 25 basis points, while Zhongtian rebar prices were raised by 50 yuan.
Time:2025-12-11
-
During the 14th Five-Year Plan, China’s steel industry is exploring a path toward reducing output while improving quality.
Time:2025-12-11
-
Multiple regions have activated emergency responses for severe pollution, and the scale of maintenance at steel mills has expanded.
Time:2025-12-11
-
Summary of the Jiangsu Steel Industry Chain Access White List; Shortage of Building Materials Specifications in Yunnan and Guizhou
Time:2025-12-03
-
Steel mills are expanding the scale of production cuts and maintenance, and steel billets in Tangshan rose over the weekend.
Time:2025-12-01
-
The NDRC is promoting measures to address disorderly price competition; this week, steel supply has increased while demand has declined.
Time:2025-12-01
-
Iron ore prices surged above $105, and the yuan-to-dollar exchange rate hit a more than one-year high.
Time:2025-11-27
-
Xi Jinping Holds Telephone Conversation with Trump; International Commodity Prices Rise
Time:2025-11-27
-
Several Federal Reserve officials signaled potential interest rate cuts, while Shagang's scrap steel prices were lowered.
Time:2025-11-24
-
Black futures fell in the night session, with electric furnace steel mills posting a loss of 117 yuan per ton.
Time:2025-11-20
-
International commodity prices fell across the board, while five steel mills raised their prices.
Time:2025-11-18
-
More construction material steel plants have resumed production, and inspection teams will gradually begin operations in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region.
Time:2025-11-17
-
Black futures fell during the night trading session, as the Simandou iron ore project will gradually ramp up its production capacity.
Time:2025-11-13
-
Xinjiang steel plants reduce production during winter maintenance, while the U.S. temporarily suspends its export control rules on penetrating technologies.
Time:2025-11-12
-
In December, Baowu Steel raised prices amid a general rise in international commodity markets.
Time:2025-11-12
-
Supply and demand for the five major steel products both declined, with electric furnaces incurring a loss of 167 yuan per ton of steel.
Time:2025-11-07
-
Steel prices remained stable overall, while coking coal futures rose by more than 1%.
Time:2025-11-06
-
The Drivers Behind China's High Growth in Steel Exports and the Resulting Structural Changes
Time:2025-11-05
-
Morning Reading: 84 New Enterprises Proposed for Entry into Scrap Steel Processing, Baosteel Adjusts Production Capacity Goals
Time:2025-11-04
-
Morning Reading: The Ministry of Commerce Highlights the Consensus Reached in China-U.S. Economic and Trade Talks, While 6 Steel Mills Raise Prices
Time:2025-10-31
-
Morning Read: China-U.S. Leaders to Hold Meeting, Fed Cuts Interest Rate by 25 Basis Points
Time:2025-10-30
-
Morning Read: "One Line, One Bureau, One Meeting" Makes a Strong Statement—Black Futures Turn Positive in Overnight Trading
Time:2025-10-28
-
Morning Read: China and the U.S. Reach Preliminary Consensus; Draft Opinions Sought on New Steel Capacity Replacement Plans
Time:2025-10-27
-
Morning Read: International commodity prices surged across the board, while supply and demand for the five major steel products both increased.
Time:2025-10-24
-
In the third quarter of 2025, Fortescue's iron ore production reached 50.8 million tons, representing a year-on-year increase of 6%.
Time:2025-10-23
-
Steel prices remain stagnant as the market awaits a breakthrough in macroeconomic conditions.
Time:2025-10-22
-
Morning Reading: China and the U.S. Agree to Hold a New Round of Economic and Trade Consultations; Steel Mills Reduce Production and Conduct Maintenance Inspections
Time:2025-10-20
-
Morning Reading: Sichuan's Steel Industry Advances Measures to Combat "Involution," While Several Steel Mills in Northern China Undertake Maintenance Overhauls.
Time:2025-10-16
-
Morning Reading: China Responds to U.S. Threat of Additional Tariffs on China, October North-to-South Steel Material Survey
Time:2025-10-13
-
Morning Reading: Two Departments Take Action to Address Unregulated Price Competition, Black Commodity Futures Turn Positive in Overnight Trading
Time:2025-10-10
-
Morning Reading: Steel inventories surged by 1.28 million tons during the holiday period; summary of performance for black commodity sectors
Time:2025-10-09
-
Morning reading: The State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission urges central enterprises to take the lead in "fighting internal involution," as rebar prices fall below 3,100.
Time:2025-09-28
-
Morning Reading: Ministry of Commerce Counterattacks Mexico's China-Related Measures; Supply and Demand Both Rise for Five Major Steel Products
Time:2025-09-26
-
After the National Day holiday, the price of hot-rolled strip steel in China may rise first and then decline
Time:2025-09-25
-
South Korea's K-Steel bill is impacting our country's steel exports, and the three major coal import ports will shut down.
Time:2025-09-24
-
Black Metal Regular Meeting: This week, the steel market showed mixed trends, while raw materials may remain relatively strong.
Time:2025-09-23
-
Midday Report: Steel prices mainly rose, with coking coal futures climbing more than 5%.
Time:2025-09-16
-
A Brief Analysis of Profit Contraction Pressure on Domestic Tinplate Manufacturers
Time:2025-09-15
-
Afternoon Report: Localized Steel Price Increase, Iron Ore Futures Drop Over 1%
Time:2025-09-11
-
Morning reading: Latest survey on steel mill maintenance impact, structural steel production capacity adjustment enters a stable period
Time:2025-09-08
-
Morning reading: Tangshan Steel Plant resumes production in batches, Trump signs US-Japan trade agreement
Time:2025-09-05
-
Morning reading: Black futures declined in the night session, construction sites in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei gradually resume work
Time:2025-09-04
-
The Breakthrough Path for Steel Enterprises under the Transformation and Upgrading of the Construction Industry
Time:2025-09-03
-
The steel market still has room to decline in September
Time:2025-09-02
-
Anti-dumping situation of foreign steel products against China from January to August
Time:2025-09-01
-
The European Union plans to eliminate tariffs on American industrial goods to alleviate the impact of car tariffs.
Time:2025-08-29
-
Reference | Interpretation of the second half market based on silicon steel supply and demand
Time:2025-08-28
-
WEEKLY SUMMARY: China's steel market slides on weak fundamentals
Time:2025-08-25
-
WEEKLY: Chinese mills' steel stocks edge down
Time:2025-08-22
-
Việt Nam imposes anti-dumping duties on Chinese and South Korean coated steel
Time:2025-08-19
-
Vietnam imposes AD duties on galvanized steel from China, South Korea
Time:2025-08-19
-
Detailed explanation of color-coated steel sheet types, colors, and applications
Time:2025-02-27
-
What is cold-rolled sheet material? A comprehensive analysis of the characteristics and applications of cold-rolled sheet.
Time:2025-01-08
-
Advantages and Applications of Cold-Rolled Sheet
Time:2025-01-08
-
Applications and characteristics of color-coated steel sheets
Time:2025-01-08
-
Detailed explanation of the function and advantages of color-coated steel plate
Time:2025-01-08
-
What thickness and width of stainless steel do you require?
Time:2025-01-08








